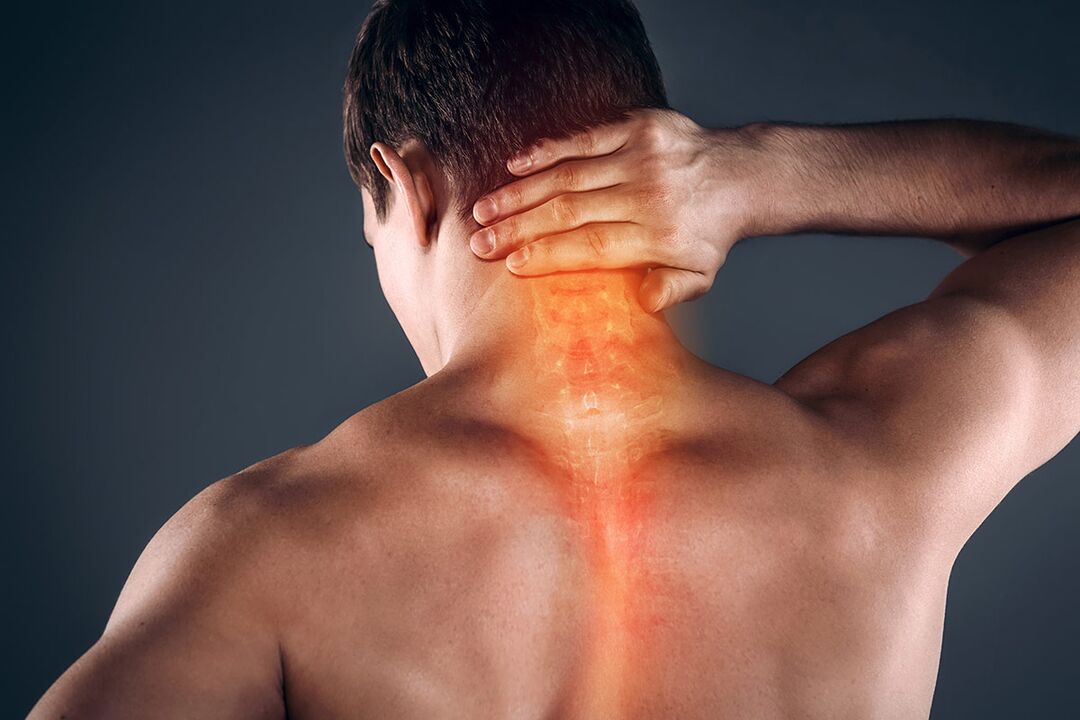
Neck osteochondrosis is a common spinal disease that affects patients of all ages. This is a degenerative change of the intervertebral disc that develops under the background of severe stress, wearing the wrong shoes, heavy physical exertion, and malnutrition.
It develops gradually, so the patient may not notice the initial symptoms immediately.
Another name for this disease is degenerative and destructive disease of the spine, which affects the vertebral body, ligaments and joint devices, and intervertebral discs.
It is also frequently diagnosed in men and women, and usually, it will develop after 30 years. According to statistics, this disease affects 50% to 80% of the population.
The main symptoms of the disease
As the pathology progresses, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis appear. They are more noticeable during the deterioration period. After noticing the first signs of the disease, it is recommended to consult a doctor, as it is often disguised as another disease, which complicates timely diagnosis. Patients usually have the following complaints:
- Severe pain in the collar area.
- There is noise and stuffiness in the ears.
- Often dizzy.
- Shortness of breath, feeling short of breath.
- feel sick and vomit.
- Blood pressure drops.
- Frequent fainting or fainting.
- Increased body temperature.
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men are not much different from those in women. The patient complained of discomfort in the occiput, sternum, and shoulder straps. You should contact your local therapist or neurologist for diagnosis.
Neck pain
One of the most common symptoms of cervical chondropathy is neck pain that affects the head and back of the shoulders. The nature of pain (pain, severe, slight tingling) directly depends on the location of the lesion and the severity of the development of the pathological process. In the initial stage, this may be a slight discomfort that does not allow you to turn your head freely in all directions. Gradually, the pain becomes chronic and limits the range of motion.
Due to insufficient blood supply to the collar area, the vertebrae deform and cause pain. In the context of this process, convulsions, anxiety and panic attacks were observed. Pain in the neck area may radiate to the shoulders or arms. Increased after sleep, sudden movements, laughing or sneezing. When trying to turn around or muscle weakness, discomfort is accompanied by characteristic tightening.
Muscle tissue spasm and poor blood circulation usually cause not only pain, but also temporary loss of neck mobility. The constant overwork spread to the entire head, and the patient began to complain of migraine attacks.
Noise and congestion in the ears
Neck osteochondrosis also manifests as ear tightness, hearing loss, and noise. All of this happens due to insufficient blood flow to the vestibular organs. This complex symptom is called the cochlea, but doctors rarely associate it with diseases in the vertebral region. Pay attention to the nature of noise and tinnitus. They are usually exacerbated when a person stays in one position for a long time or tries to change it.
Patients with hearing problems will turn to an otolaryngologist for help. If there are concomitant diseases of the condition, such as facial numbness and restricted neck movement, additional consultation with a neurologist is required to confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause.
Headaches and migraines
The main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men are rarely accompanied by frequent headaches; women are more susceptible to these symptoms. If the muscle tissue is not elastic enough to keep them in their natural position, the vertebrae in this area will continue to bear excessive pressure, which will cause them to gradually deform. Because the symptoms are not specific, it is more difficult to determine the cause of the head pain. Attacks can be triggered for the following reasons:
- Cerebral vasospasm.
- The nerve endings of the cervical thoracic spine are compressed.
- High blood pressure.
- Acute violation of venous outflow.
- Increase fatigue.
- Being in an unnatural posture for a long time.
Headaches are exacerbated during exacerbations and among patients, including men. In essence, it can be a persistent, dull seizure or pulsation. In the elderly, this symptom requires close attention because it may be related to initial stroke, angina, heart attack or arterial hypertension. Therefore, these conditions must first be ruled out before starting the treatment of osteochondrosis.
For heart diseases, patients also complain of chest compression, which is an irregular heart rhythm, which enables doctors to distinguish the condition in time. Headaches are accompanied by nausea and shortness of breath, so an electrocardiogram must be performed.
Dizziness
When osteochondrosis progresses to grade 2 or above, there is often impaired coordination and frequent dizziness. This is due to degenerative changes of the vertebrae, spasms, and nerve endings squeezing. The brain cannot get the amount of oxygen it needs, which negatively affects the function of the vestibular organs. Due to conditional deviation, the symptoms are:
- Systemic vertigo. They manifest as the sensation of rotation of the whole body and surrounding objects. Dysfunction occurs due to vestibular organ dysfunction, weakened muscle tissue and receptors located in the joints.
- Non-systemic vertigo. In addition to being unstable, the patient also feels nauseous, which is an uncertain state of an upright posture. There is usually no circular rotation.
Dizziness is a serious symptom, and you should seek medical attention immediately. If there is shoulder numbness, facial muscle tissue numbness, loss of consciousness, urgent hospitalization is required.
Shortness of breath and lack of air
Another serious symptom of advanced shoulder osteochondrosis is a constant lack of air. Respiratory problems are caused by compression of nerve endings and receptors, which cannot transmit impulses from the pharynx to the esophagus. Shortness of breath occurs when the vertebrae are displaced, which can be aggravated under pressure, and accompanied by a lump in the throat. After taking sedatives, his health returned to normal.
Insufficient air can cause nerve root syndrome. Diaphragm spasm affects the depth and rhythm of breathing. The patient becomes depressed, has difficulty breathing, and has memory and concentration problems. This symptom of osteochondrosis requires immediate help because it can cause many serious complications. The doctor will choose the medicine individually according to the condition.
Nausea
In the neck area, there is a large accumulation of nerve endings, and the arteries responsible for delivering nutrients to the brain pass through it. With osteochondrosis, protrusions and intervertebral hernias are gradually formed, which affect blood pressure, so the patient feels nauseous.
Long-term impairment of normal blood circulation can cause vomiting, loss of consciousness, and lead to stroke and disability. Therefore, symptoms that have nothing to do with nutritional errors require immediate medical attention.
High blood pressure
For cervical osteochondrosis, a typical symptom is pressure jumps during the day. Failure to maintain increased or decreased blood pressure for a long time is a characteristic sign of degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc. The daily dynamics of blood pressure are sudden, because the stimulation of nerve endings is reflexive and can cause short-term spasms of blood vessels. A notable feature of increased pressure in cervical osteochondrosis is:
- Headache;
- Chest discomfort;
- Reduced sensitivity in the collar area;
- Muscle tension after being in one position for a long time.
All of these are taken into consideration when making a diagnosis. The rapid deterioration of the condition and the sudden change in pressure are the basis for the patient to be hospitalized and to help him in the hospital environment.
Visual impairment
Cervical osteochondrosis often causes unpleasant symptoms such as diplopia, blinking, and "flies". This indicates the seriousness of the procedure and the need to see a doctor. In the context of the destruction of connective tissue in the vertebrae, the following diseases may occur:
- glaucoma. The patient was diagnosed with elevated intraocular pressure and damage to the optic nerve. It is impossible to completely exclude pathologists, and stable remission can only be achieved through complex treatments.
- cataract. This pathological process leads to the destruction of the lens. These changes are related to the acute injury of metabolic processes and oxygen supply to the brain. The first sign of this disease is the appearance of "flies". Beginning treatment in time can help protect the patient's vision.
- Claude Bernard-Horner disease. One of the reasons for the appearance of the disease is considered to be hypoxia in the occiput. The main sign of a pathological condition is decreased pupil response or differences in pupil sizes of different eyes. Some patients complain that they cannot fully close their eyes and rest overnight, and their twilight vision is also affected.
The ophthalmologist prescribes a treatment plan after a thorough examination. But treatment is only carried out in a complex designed to eliminate the cause of violations. Only in this way can the problem be effectively dealt with.
Pharynx problems
Degenerative changes in the cervical spine can cause swallowing problems. The patient complained of a lump in the throat, sweating, foreign body sensation in the throat, and itching. There are signs that the main nerves and blood vessels from the spinal cord are malfunctioning. However, the symptoms are not considered characteristic, and pathological disorders such as inflammation and swelling can be observed.
Body temperature changes
As osteochondrosis develops, it becomes the cause of increased body temperature. Such symptoms can occur when the vertebral artery is damaged, spinal canal stenosis, or intervertebral disc herniation. It can cause neurosis and accompanying changes in neurological diseases. Under the background of increased temperature, the tongue or hands will be numb, the lymph nodes will become inflamed, and the tongue will burn.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis in different stages
The signs of cervical osteochondrosis depend to a large extent on the development stage of the pathology, the compression force of the nerve endings and the deformation process of the intervertebral disc. It can cause symptoms of vertebral artery compression and violation of blood flow to the brain. Compressed nerve endings can cause severe neuropathy. The severity of the signs directly depends on the stage of development of the disease:
- initial. The degenerative process of the intervertebral disc can be ignored by the patient. It is difficult to notice the initial changes because these changes can be mild headaches (females feel more intense), neck discomfort, slight loss of vision, or loss of sensitivity in the collar area. At this stage, patients rarely see a doctor and attribute symptoms to fatigue, lack of sleep, or stress.
- second stage. As the pathology progresses and intervertebral disc herniation appears, more obvious symptoms appear. The destruction of the annulus will affect the movement of the head, and they become more limited. In addition, patients began to complain of tinnitus, impaired visual function, neck pain with characteristic tightening, swallowing problems, sleep disturbance, and decreased reflex clarity. Keeping the head in one position can cause severe discomfort, which requires consultation with a doctor.
- The third phase. The intervertebral hernia gradually formed, the annulus fibrosus was completely destroyed, the vertebrae were deformed, the joints were displaced, dislocated, and unstable. The patient complained of acute neck pain, obvious shoulder syndrome, paralysis of the upper limbs, no tendon reflexes, and impaired scalp sensitivity. This is the severe stage of the disease and requires complex treatment.
Osteochondrosis is a chronic systemic disease with multiple symptoms. The reason is always hidden in the compression of nerve endings, circulatory disorders and intervertebral disc deformation. Herniation, hernia, and displacement gradually lead to loss of mobility of the vertebrae.
Age directly affects the severity of symptoms. The older the patient, the stronger the changes in connective tissue and bone tissue. This is caused by weak muscle fibers, nutritional deficiencies and chronic inflammation in the body.
Patient testimonials
Cervical osteochondrosis is a common disease, because the excessive activity of this segment causes the nerve root to continue to bear pressure. Detecting pathology in time can avoid serious complications, so many people read patient comments and compare them with symptoms.
Female, 35 years old
"We suspected osteochondrosis almost immediately because I often suffer from headaches and cannot turn my neck. But the diagnosis was made after X-rays. Because the treatment did not get a normal result, and the pain was still periodicWhen it appears, the computed tomography is still ahead, and it will confirm or deny the progress.
Woman, 42
"As the symptoms echoed with my gastritis, the doctor was unable to determine osteochondrosis for a long time. I felt nauseous from time to time, but I attributed this to a nutritional error. Only after fainting did I see the doctor and started looking for the problem. Neck. The discomfort of the neck is not very painful in the initial stage. As the pathology progresses, the pain will be felt by itself. The treatment is only performed after the CT scan. The treatment is gradually effective. "
Male, 36 years old
"Neck osteochondrosis developed due to the peculiarities of the industry, but they could not be determined immediately. At first, my eyesight declined, I immediately blamed night eye fatigue, and then started dizziness and neck pain, but because of myI drive a lot and this does not bother me. The diagnosis has been made in almost 3 stages. At that time, the pressure began to surge and the problem started with general health. The treatment has not yet achieved significant results. "
No self-diagnosis without laboratory and instrument research is strictly forbidden. Any information should only be used as a comment.
Cervical osteochondrosis presents a large number of symptoms, but most of them are easily confused with similar pathologies. Therefore, it is recommended to comprehensively consider the main complaint of the patient and make a differential diagnosis in order to identify the disease in time and carry out the correct treatment, including physical therapy, gymnastics and drug therapy.